Posted
on
in
Operating System
• 421 words
• 2 minute read
Tags:
Operating System
Clock Speed, You might have heard this term often when buying a new laptop or smartphone. But what does it actually mean?
The CPU has an internal clock (a clock signal generate by oscillator circuit) that continuously ticks, so with each tick CPU performs some part of an operations such as fetching, decoding or executing an instruction.
The speed or rate at which this clock ticks is called as Clock Speed. Think of it as processor’s heartbeat.
What Happens During Each Tick?
This isn’t a modern computer concept, it’s the core principle behind how all processors work, from simple calculators to advanced computers.
CPU executes instructions in three fundamental stages:
- Fetch – Get the next instruction from memory
- Decode – Understand what the instruction means
- Execute – Perform the action
Every clock tick advances the CPU to the next action.
Modern CPUs pipeline these Fetch, Decode & Execute stages, but the basic concept remains the same.
Now let’s Visualize this
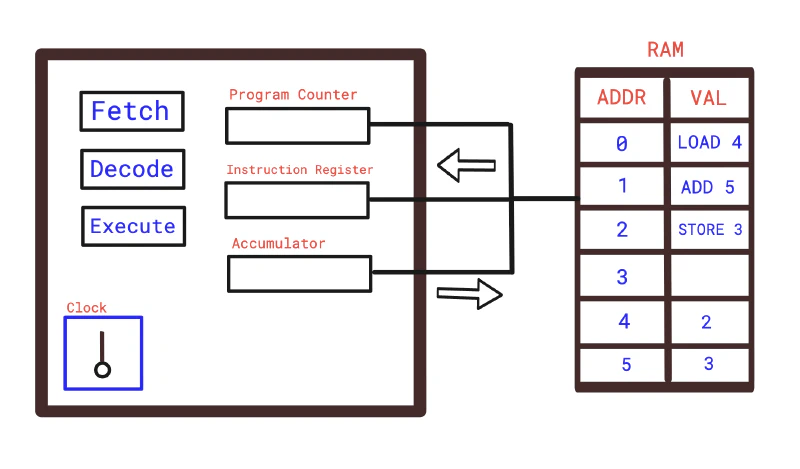
- Initial State: Assume the CPU is IDLE. Nothing is loaded yet.
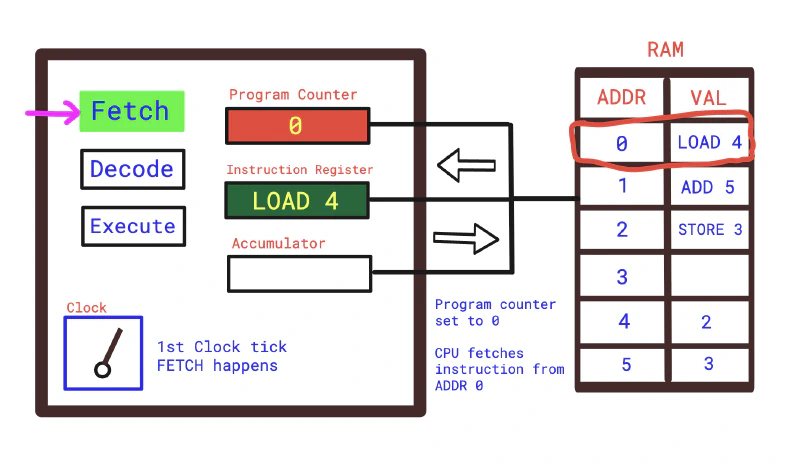
- First Clock Tick — Fetch: CPU reads the next instruction from memory, the program counter set to zero. It fetches the instruction at address zero and puts it into the instruction register.
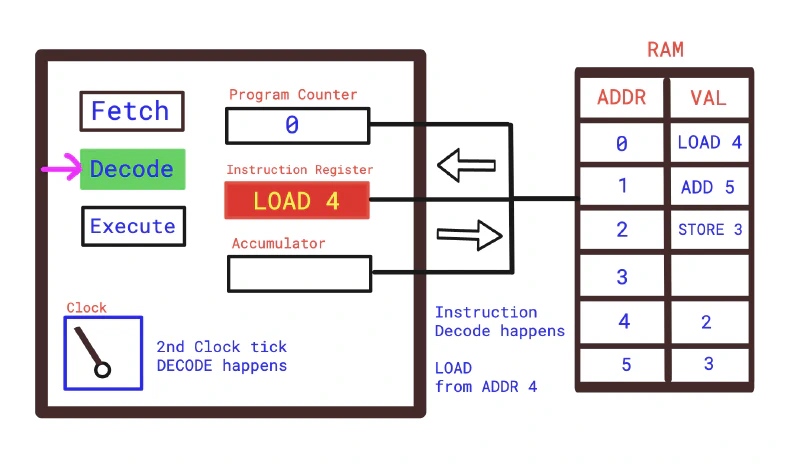
- Second Clock Tick — Decode: CPU Decodes the fetched instruction.
LOAD 4
First part is the instruction and the second part is the memory address.
- LOAD → the operation
- 4 → the memory address to load from
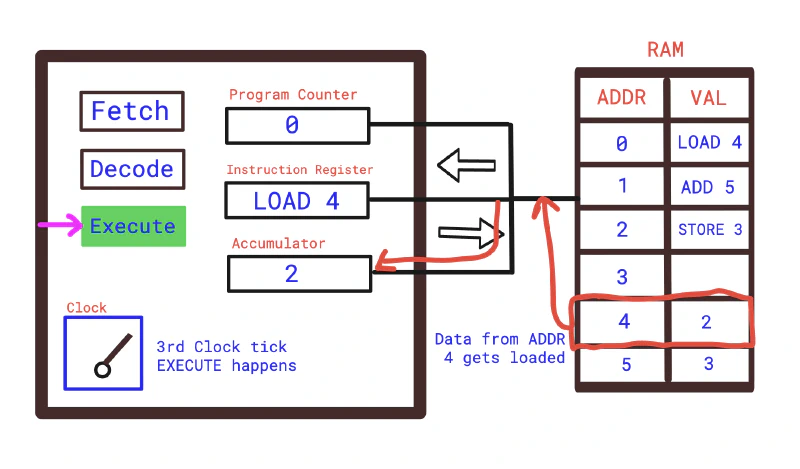
- Third Clock Tick — Execute: CPU Executes the instruction. It loads the value stored at memory address 4 into the Accumulator.
After That…
The Program Counter increments to 1. The next clock tick triggers Fetch of the next instruction at memory address 1. And the cycle repeats endlessly: Fetch → Decode → Execute → Fetch → …
Measurement Unit
Its usually measured in hertz (Hz).
- 1 Hertz (Hz) = 1 cycle per second
- 1 Megahertz (MHz) = 1 million cycles per second
- 1 Gigahertz (GHz) = 1 billion cycles per second
Example: A 3.5 GHz processor executes 3.5 billion cycles per second.
The Clock Cycle
Every CPU runs to the rhythm of its clock. Each tick of this clock called a clock cycle, moves the CPU forward through its instruction stages fetch, decode and execute.
Conclusion
This is the story behind the clock speed, So when you see the label or hear 2.4 GHz or 5.0 GHz, you’re looking at the heartbeat of the CPU.
